Thailand's tableware ceramic industry has been developed from the small & medium-sized industry to serve domestic demand as well as to decrease imports. The annual export turnover of tableware ceramic totalled more than 4 billion baht over the past one to two years.
The total market value of the tableware ceramic industry grew by an average of 17.5% a year during 1995-1998 and declined by 9% or 5,508 million baht in 1999. Despite the improving economy, the financial and investment sectors have been consistently slowing down. This is due to the decline of domestic demand (local sales and imports) and exports. The total market value of the tableware ceramic industry in 2000 is projected to rise by 7% year-on-year, and 80% of which are for the export orientation.
About of 90-100 manufacturers have currently operated in the tableware ceramic business, most of them have produced Stoneware and Earthenware. Both kinds of products have a relatively tough competition because the production doesn't need a large amount of investment capital. The production requires neither a complicated technique nor a highly skillful technician. However, Stoneware and Earthenware have a lower margin compared to Porcelain and Bone China.
The tableware ceramic industry uses clay as the main ingredient, which can be obtained in the country, except some materials that manufacturers need to import due to a typical attribute such as bone ashes, etc. Nevertheless, the small and medium-sized manufacturers in particular currently prefer to use instant clay or compound clay in the production process owing to convenience and timeliness. Meanwhile, other materials are necessary to import from abroad, such as color or pigment and glaze or frit, etc. The main machinery used in production, namely a ceramic kiln, a clay mixing machine, a forming machine and molds, are available in the country; while labor forces can be recruited nationwide.
The total investment capital for the tableware ceramic industry depends on the production category. The initial investment capital is mostly spent on raw materials and wages while the machinery doesn't cost too high. At the same time, the overhead expenses are mainly the energy cost (a gasoline or electricity) for firing ceramics, followed by depreciation, and interest expenses in case of borrowing for operation.
Marketing
Demand: Present and Future
The tableware ceramic has been divided into four core categories. Firstly, Earthenware is a thick and finely product, but it has a porous attribute that can absorb the water such as a chicken brand bowl, a rice dish or a noodle bowl, etc. Secondly, Stoneware is a solid and thick product. It is usually produced in an opaque glaze. Thirdly, Porcelain has a better quality than the above two products, but it costs more expensive. Porcelain consists of the opaque glazed porcelain and the transparent glazed porcelain. Its attributes are solid and water-resistant. Porcelain has been usually produced the slim and shiny glazed ceramics. Lastly, Bone China is the highest quality and most expensive product among all kind tableware ceramics. It is white, shiny, slim and lightweight. Bone China is the best quality of strength as made of animal bones or bone ash.
The total market value of the tableware ceramic industry during 1995-1998 grew by an average of 17.5% a year. The export markets (about 75-80% of total market value) expanded by an average of 22% a year, totalling 5,151 million baht in 1998. At the same time, the domestic market growth (local sales and imports) was unchanged at 930 million baht. Despite the improving economy since 1999, but the financial and investment sentiments have been consistently slowdown, particularly the hotel, restaurant and food store business. Meanwhile, the purchasing power of consumers becomes lower contributing to the demand shrink of tableware ceramic by 9%, accounting for 5,508 million baht. About 820 million baht of total sales generated from domestic market, or dropped by 9% from last year. For imports, both volume and value are expected to rise from a year earlier, totalling 340 tons or valuing 38 million baht. The import prices are likely to decline by 46% from a previous year as a result of the market dumping of cheaper goods from China, Indonesia and Malaysia.
The export value of tableware ceramic in 1999 is expected to slump by 9.7% year-on-year to be 4,650 million baht. On volume, the export slid by 1% only amounting to 58,800 tons. This was partially due to the tougher competition in export markets and contributing to the downtrend of export prices by 9% from a year ago. Of total export value, about 36% generated from Porcelain and Bone China while the rest of 64% came from Earthenware and Stoneware. Nevertheless, the price of porcelain and bone china tends to decrease in a higher ratio than of earthenware and stoneware because of the design and quality development to meet the upper and middle-class markets demand. The main export markets of tableware ceramic are United States, Japan, Australia, and such the European countries as England, German, Italy, etc.
The total market value of tableware ceramic in 2000 is projected to grow by 7% from a year earlier to be 5.9 billion baht. Of total market value, above 80% of tableware ceramic industry are export-oriented. The export growth is projected to increase by 7.5%, valuing 5 billion baht because of the improvement of product design and quality to meet the market demand and the expansion of the emerging market like the Middle East. Domestic consumption (domestic sale and imports) will rise by 4.9% to 900 million baht in parallel with the improving economy, finance and investment.
Present Manufacturers
A total of 90-100 manufacturers have currently operated in the tableware ceramic industry. Most of them are small and medium-sized. The tableware industry is the oriented-export production, accounting for above 70%. The production is mostly Stoneware and Earthenware. The competition is relatively high compared to Porcelain and Bone China because they require no high investment capital, non-complicated production technique and no high skills. Stoneware and Earthenware, however, gain a lower margin compared to Porcelain and Bone China. Currently, quite a few manufacturers have produced Porcelain and Bone China such as Royal Porcelain Co., Ltd. and Siam Fine China, a subsidiary of Jalaprathan Cement and Patra Porcelain Co., Ltd., etc. A large manufacturer usually locates a plant nearby Bangkok due to convenient transportation while the small and medium-sized manufacturers scatter their plants in upcountry, especially in the north such as Lampang and Chieng Mai because of easy access to raw material sources and low wages.
List of Major Tableware Ceramic Manufacturers
Large Size Registered capital (baht)
Siam Fine China Co., Ltd. 700,000,000
Thai Ceramics Co., Ltd. 422,000,000
Patra Porcelain Co., Ltd. 330,000,000
Royal Porcelain Co., Ltd. 300,000,000
Medium and Small Sizes
Thai Porcelain Co., Ltd. 109,000,000
Thai Pottery Industry Co., Ltd. 80,000,000
Pongpaibul Industry Co., Ltd. 70,000,000
Kasalong Ceramics Co., Ltd. 68,571,000
Eastern Chinaware Co., Ltd. 48,350,000
Two way Ceramics Co., Ltd. 35,000,000
Source: Department of Industrial Works and Board of Investment (BOI)
Distribution Channels
The clients of tableware ceramic are divided into three categories that are:
1.! Lower class: a small-sized food store or trolley and a low-income household. The favored products are mostly Stoneware and Earthenware.
2.! Middle class: hotels, a medium-sized food store, restaurants and a medium-income household. The popular products are usually Stoneware and Porcelain.
3.! Upper class: a five-star hotel, a large restaurant, aviation and a high-income household. Porcelain and Bone China are mostly in favor.
Distribution channel in domestic market can be classified as follow:
1.! Directly distribute to the main clients such as a five-star hotel, a large restaurant and aviation. The products are relatively expensive and are made to order, etc.
2.! Distribute through a showroom and a department store
3.! Distribute through selling agents, wholesalers and retailers in Bangkok and the provinces, etc.
4.! Distribute through a booth display and a product exhibition
5.! Distribute through a promotion of other kinds of products
For overseas market, manufacturers will either sell the products through the selling agents or take orders directly from foreign clients. Clients may probably create their own designs.
Production
Raw Materials and Sources
The main ingredients used in production process are as follow:
1.! Clays consist of various mixture in different proportion depending on product category, for example, kaolin or fine white clay, sticky kaolin or fine white clay, feldspar, quartz and limestone. Raw clays are generally available in upcountry such as Lampang, Utaradit, Ranong, Chonburi, Lopburi, Kanjanaburi, etc. Bone China needs some imported materials like the high-quality bone ashes, etc. The production process starts with adding above materials together in a ball mill for fine grinding. However, manufacturers currently have an option to use a wide variety of instant or compound clays up to desired products for more convenience and speediness. Instant Clay distributors are Compound Clay Co., Ltd. and Clay and Minerals (Thailand) Co., Ltd. The price is subject to the clay category. For example, clays for Stoneware production cost five baht per kilogram, for Porcelain cost at 15-17 baht per kilogram and above 20 baht per kilogram for Bone China, etc.
2.! Color or Pigment is the main ingredient of production and enables the beautiful and attractive products.
Manufacturers commonly use the oxide substances to draw a pattern on ceramics before firing to give colors, namely, cobalt oxide (blue color), copper oxide and chromic oxide (green color), ferric oxide (brown color up to dark green), Manganess Oxide (brown color). In addition, they can use different kinds of instant colors in production. For instance, the Underglazing Color is used to draw a pattern before drying and passing into a glaze slip. The Overglazing Color is used to decorate the glazed ware. After painting, the ware will be taken to firing again. The color of overglazed ware is usually brighter than of underglazed ware. Nevertheless, the overglazing color has not been used in food container production because some kinds of glazing color may be solvent in acetic acid.
Current distributors of ceramic colors are Cernic Co., Ltd., Chakramon Ceramics Co.,
Ltd., etc. The materials used in the color and instant color production are mostly imported from abroad such as Japan, United States and European countries, etc. At the present, manufacturers prefer to use a sticker for decoration due to convenience and promptness. Some stickers are painted with overglazing color, but some painted with underglazing color. After firing, the sticker will be fused onto the surface of desired product.
3.! Glaze helps even the product surface and make it easy for cleansing. The glazed ware is beautiful and endurable for damages of acid and sodium chloride. The glaze is divided into several categories classified by attributes such as glaze, frit, opacity and glazed surface (the surface of glazed ware will be callous like an eggshell. The glaze enables a shiny surface, callous and semi-callous). There are several glazing methods such as immerging, pouring, plating, brushing, etc., but the most popular technique is immerging. The glaze preparation can be conducted in a different way depending on desired product and surface. Operators in the tableware ceramic business presently can buy the ready-to-use glaze from the manufacturing companies, distributors or even import from abroad up to desired attributes. The glaze producer is Ceramic R-US Co., Ltd, etc.
4.! Forming Mold is probably made of a plaster for a mass production and the same design or in a case that some kinds of ceramics are produced neither by hand nor by machine.
5.! Refractory Box/Fireproof or Called "Jhor" is used to obtain the glazed ware for firing in a kiln. The box enables the ware gain heat totally and regularly, especially from gasoline or charcoal kiln. At present, the product can be placed on the pad called silicon carbide before baking.
Cost Structure of Tableware Ceramic Industry
Category Percentage
1. Raw materials 22
- Domestic Raw Materials 65
- Imported Raw Materials 35
2. Wages 40
3. Overhead Cost 30
4. Depreciation and Others 8
Total 100
Source: Interview manufacturers
Production process
Preparing clays/mixing instant clays with water
Forming by hand, platform or throwing and casting up to appropriation
Decorating and leave the clay dry
Dehumidifying clays at about
1st Firing (Biscuit Firing) 900-950C for 4-8 hours
(depending on category)
Drawing/copying
Glazing
Glaze fused onto the surface of the ware at about 1000-1350C
2nd firing (Gloss firing) for 6-12 hours.
Checking the quality and selecting
Packing/Distribution
Source: Interview manufacturers
Machines for Production
The machinery used in the tableware ceramic industry are as follow:
1.! A kiln consists of a brick kiln and a fiber kiln. A variety of fuels have been used in firing process such as bunker oil, gasoline, electricity and coal, etc. However, the kiln using fiber as a heat insulator has got a promotion and has the high popularity. It is fuelled with both electricity and gasoline. Meanwhile, imported kilns mainly come from Australia.
2.! A clay-mixing machine is generally available in domestic market. In addition, the powder-mixing machine for the bakery industry has been applied to mix the clays or made to order up to desire, and it doesn't cost the high price.
3.! A forming machine and a machine for pressing the processed clay into plates before shaping.
Investment and Finance
The tableware ceramic industry should locate the plant nearby the raw material sources or selling market. The total investment capital and equipment used in the tableware ceramic production, which require 60 tons of instant or compound clays per year and 8 working hours per day are identified as follow:
Initial Investment
1.! The registered capital and initial capital totalling 2-2.5 million baht
2.! Investment in permanent assets such as land and constructions. The area of production requires 100-150 square wah. For a small business, operators usually rent the plant for production, accounting for 5,000-10,000 baht per month up to location. The plant should open to the fresh air passing throughout.
3.! Costs of machinery
3.1!Forming machine is commonly produced in the country. The production needs 3-4 machines, each of which prices at 40,000-60,000 baht.
3.2!Clay-mixing machine: the price varies in size and attributes starting at 5,000 baht up to above 30,000 baht. The machine may probably be made to order up to desire. For a medium price machine, it values at 10,000 baht.
3.3!Two ceramic kilns fuelling with either gasoline or electricity. The price begins at 350,000 baht up to above 800,000 baht up to size. For a 2.5 cubic meter ceramic kiln, the price is approximately 650,000 baht (the price will be cheaper, amounting to 429,000 baht under a project of the Energy Efficiency Institute Thailand Foundation).
4.! At least one used car for transporting goods. The price ranges between 300,000 baht and 500,000 baht.
5.! Cash flow is spent on raw materials, wages and production expenses totalling 300,000 baht.
Personnel: a small tableware ceramic business requires a total of 25 employees.
1.! A total of 20 plant workers consist of
1.1!Clay-mixing technician
1.2!Forming and casting technician
1.3!Pattern drawing technician
1.4!Product delivery driver
1.5!Kiln control workers
1.6!Decorating and packaging workers
2.! Office workers and administrative officers: For a small business, administration manager is mostly the business owner. About 3-4 workers are general workers and clerks.--(next)
Tableware Ceramic Industry (2)
Source - Department of Industrial Promotion (Th/Eng)
Saturday, January 15, 2000 19:00
24068 XENGLISH XFF XART XGOV XLOCAL V%GOVL P%DIP
Annual Expenses
Cost of Production
1. Cost of Raw Materials 625,000 baht/year
(For 60 tons of instant clays per year, a loss is about 15 percent of total production)
- Instant or Compound Clays 300,000 baht/year
- Glaze 180,000 baht/year
- Color or Pigment 110,000 baht/year
- Design 35,000 baht/year
2. Wages 1,950,000 baht/year
3. Cost of Depreciation 240,000 baht/year
4. Overhead Costs 815,000 baht/year
4.1 Utilities
- Water 45,000 baht/year
- Electricity 240,000 baht/year
- Gasoline (for two kilns) 450,000 baht/year
- Telephone 45,000 baht/year
4.2 Transport Cost
- Oil 35,000 baht/year
5. Other Expenses
5.1!Hire for making an account 70,000 baht/year
5.2!Machinery maintenance 30,000 baht/year
5.3!Interest expenses - O/D 40,000 baht/year
5.4!General expenses -- wasteful materials 30,000 baht/year
The average profit is approximately 15-20% of total sale.
Note: Total sale is approximately 4.5-4.75 baht/year
In addition, the establishment of a product design company and the hire of production may be one of attractive ways for investment and may be proper with the small operators due to less investment capital and non-complicated technique. They usually produce Porcelain and are able to manufacture under their own trademark. The initial investment capital is rather low, totalling not more than 1 million baht.
Other advantages are no machinery venture, no plant workers, no raw material stock, no risk for the loss of production, no risk for demand drop, etc.
Expenses for initial investment are as follow:
1.! Rents for office building up to location
2.! About 4-5 product design employees, graduated in product design is preferable, especially in ceramics. At least one experienced employee is needed. The salary ranges between 20,000 and 30,000 baht per month. Outside workers may seldom be hired to create a variety of product designs. The business also needs a marketing officer to expand the market especially in overseas.
3.! The necessary equipment are such a computer for graphic design, a small ceramic kiln for producing a product sample (each prices about 20,000 baht), 1-2 forming machines, a sticker machine for a product model (each values between 200,000 and 300,000 baht). However, for an initial investment, operators are not necessary to buy a sticker machine, but they can hire other companies at 10,000 baht per design.
4.! Cash flow is the largest expenses due to the hire of production. The down payment for hire is about 30-50 percent of total wages. In addition, there is a mold expense for a new product. The price ranges between 10,000 and 100,000 baht per design up to difficulty or simplicity as well as the production volume.
Operational Process
Creating a design and a pattern
Sticking on to the surface of the ware
Making a sticker (hire/hand-made) before firing to get the desired product and color.
Making a product presentation to clients.
Having the plant evaluate the product
At least 3-4 designs should be displayed sample to determine the selling price.
It may be done in form of brochures.
Negotiating the price, design and volume
Hiring for production, mostly takes of orders about 30 days
Inspecting and shipping
Source: Interview manufacturers
The investment should concentrate on uniqueness and a wide variety of designs. Study on a trend of a product design in favor of the market is needed for the business efficiency. For export-oriented production, the average profit is relative high because operators can set a high price if the design meets the market demand. Nevertheless, for domestic sale, operators usually earn a lower average profit due to less price competitiveness and rapid imitation. Thereby, they should hire a firm offering a low price and create a unique design. Operators should make a copyright and ask for a patent for their own products and designs.
Appendix
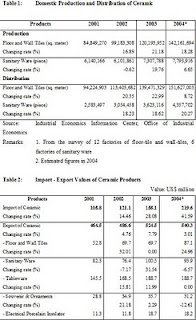
Table1: Export of Tableware Ceramic in 1995-1999
Year Quantity % Change Value % Change
(tons) (million baht)
1995 46,329.20 -3.84 2,815.28 1.06
1996 38,928.20 -15.97 2,740.57 -2.65
1997 48,507.10 24.61 3,759.21 37.17
1998 59,396.12 22.45 5,151.08 37.03
1999 (Jan-Jun) 27,223.70 0.06 2,143.57 -17.25
Source: The Customs Department
Table2: Major Export Markets in the First Half of 1999
Country Percentage
1. United States 36.40
2. United Kingdom 12.70
3. Germany 7.60
4. Italy 6.70
5. Japan 4.60
6. Others 32.00
Total 100.00
Source: The Customs Department, calculated by SCB Research Institute
Table3: Import of Tableware Ceramic in 1995-1999
Year Quantity % Change Value % Change
(tons) (million baht)
1995 347.10 45.20 17.25 2.80
1996 371.00 6.90 16.83 -2.50
1997 1,841.70 396.40 71.23 323.30
1998 140.40 -92.40 29.12 -59.10
1999 (Jan-Jun) 181.40 248.90 20.76 47.50
Source: The Customs Department
Table4: Major Import Markets in the First Half of 1999
Country Percentage
1. Japan 51.34
2. China 38.06
3. Malaysia 2.32
4. France 2.14
5. Taiwan 0.82
6. Others 5.32
Total 100.00
Source: The Customs Department, calculated by SCB Research Institute
Domestic sale
Table5: The Domestic Market Value of Tableware Ceramic in 1996-2000
Year Market Value % Change
(million baht)
1996 920 0.07
1997 990 7.61
1998-e 900 -9.09
1999-e 820 -8.89
2000-f 850 3.42
Source: Compiled by SCB Research Institute
Note: e = estimated, f = forcasted
Selling Price
The price is subject to the product category, quality, size, style and design. The medium and high price products have usually been sold in a different set such as 16, 20, 40, 45 pieces a set, etc. Of all tableware ceramics, Porcelain is the most expensive product.
Sources of Machinery
Table 6: List of Manufacturers and Distributors of Machine and Equipment
Company Address
Inter Kilns Industry Co., Ltd. 59/24 Soi 85 Petchkasem Rd., Omnoi;
Kratumban, Samutsakorn Tel. 811-0604-5
Somsak Lathing Mill 516 Moo 10, Chompu, Muang, Lampang,
Tel. (054) 346433-4
Trimurati Associates and Corporation 15/432 sukumvit Rd, Samrong Nua, Muang,
Samutprakarn, Tel. 749-2822
Ceramic Consultant and Supply Co., Ltd. 251 Seri Thai Rd. Kannayao, Kannayao,
Bangkok, Tel. 379-9677
Kilns and Art Limited Partnership 41/5 Moo 9 Bang Pra, Sri Racha, Chonburi
Tel. (038) 770-052
Teamtec and Engineering Co., Ltd. 78/6 Moo1, Ram Indra Rd., Ta Raeng,
Bang Ken, Bangkok, Tel. 900-5524
Tai Hong E Co., Ltd. 66/36 Moo 13, Bang Pakong,
Chacheongsao, Chacheongsao, Tel. (038) 834-110
Lampang Chain Service Limited Moo6, Toong Ngam Sub-district, Serm
Partnership Ngam District, Lampang
Acme-inter Marketing Co., Ltd. 49/1 Sukumvit 91 Bangkok, Tel. 332-2270-2
Somkiat Supply Limited Partnership 71 Onnuch 64, Saun Laung, Bangkok,
Tel. 721-0425-5, 721-0653-4
Source: Energy Efficiency Institute Thailand Foundation
Note: The first 8 names are members of the Project for the Promotion of the Use of Highly Efficient Kiln.
Rules and Regulations
1.! Tariffs
- Raw materials: clays used in the tableware ceramic industry carries 5 percent of import duties. Taxes on color and glaze are set at 10 percent while the animal bone ashes are at 35 percent.
- Machinery and kiln carry 5 percent of import duties
- Instant product carries 30 percent of import duties
2.! Permission for Plant Establishment.
3.! Application of Investment Promotional Privileges
Privileges and incentives will be provided to the production of Stoneware, Porcelain, and Bone China according to the promotional criteria of the Board of Investment (BOI). The total investment capital is set aside at least 1 million baht. The promotional privileges will be granted to the plants located in zone 2 and 3. (If located in zone 1, the production must be export-oriented not less than 80 percent of total sales).
For a promotional zone 3, the plant will get the eight-year exemption of corporate tax and the five-year exemption of import duties for the export-oriented production, etc.
4.! Application for Standard Quality System
The quality control system of tableware ceramic industry has been divided into many categories so as to make consumers more confident of the hygienic standard. Most standards are involved with industrial product standards of the Thai Industrial Standards Institute, Industry Ministry. Industrial standards are identified below:
Raw Material Standard: such as TIS 485-2526 -- kaolin for terra-cotta industry.
Product Standard: TIS 564-2528 -- ceramic food containers: Porcelain. No.601-2529 -- ceramic food containers: Earthenware. TIS 602-2529 -- ceramic food containers: Stoneware
Permission for a certificate of quality control standard consists of 5 stages as follow:
1.! Making an inquiry: Operators who prefer a certificate of quality control can make inquiries to the Industrial Standards Institute.
2.! Submitting an application form: Operators submit the application form and related documents for consideration of the Industrial Standards Institute.
3.! Evaluating: The Industrial Standards Institute will examine the documents involving the quality system under the standard of the quality management system. Then, the plant inspection will be conducted to evaluate the operational efficiency. If any mistake found, the improvement must be done. If the operation process is acceptable along the rules, the committee will consider a certificate approval.
4.! Granting a certificate: Operators will be granted a certificate after the quality control system of the plant has been already approved.
5.! Monitoring: The Industrial Standards Institute will regularly monitor the plant to ensure the maintenance of quality control system.
5. Copyright and Patent Registration
In case of a new product, manufacturers and designers should make a copyright and ask for a patent to prevent the product imitation. Manufacturers need to apply for the copyright at the Department of Intellectual Property, Commerce Ministry. The fee prices at 500 baht for each application. The protection of intellectual property will take effect since the period of application submission. For further details, please call at 547-4637.
Other Sources of Information
1.! Organizations supporting and promoting the industrial sector, especially aim to assist the Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
1.1! Organizations financing loans and providing a credit guarantee such as the Small Industrial Finance Corporation (SIFC) (phone number: 642-5207), the Industrial Finance Corporation of Thailand (IFCT) (phone number: 253-7111), the Department of Industrial Promotion (phone number: 202-4405-50), the Small Industry Credit Guarantee Corporation (phone number: 308-2741), the Export-Import Bank of Thailand (EXIM) (phone number: 271-3700, 278-0047), etc.
1.2! Organizations providing the human resources development, technology and management such as the Department of Industrial Promotion (phone number: 202-4405-50), the Department of Skill Development (phone number: 248-3393), Thai Industrial Standards Institute (phone number: 202-3300-3304) and the National Productivity Institute (phone number: 271-2939)
1.3! Organizations supporting investment and marketing such as the Board of Investment (BOI) (phone number: 537-8111) and the Department of Export Promotion (phone number: 511-5066-77)
2.! The ceramics industry including the production of tableware ceramic has been promoted by the Energy Efficiency Institute Thailand Foundation (phone number: 642-7090-6 ext.211, 220). The industry also gets a three-year promotion of Energy Conservation Promotional Fund, the National Energy Policy Office (NEPO) starting from October 1996 to October 1999. However, the promotion period has been expanded until July 2000. The fund will provide the financial support to make or buy the kiln at a maximum of 34 percent of the whole price. The kiln must be guaranteed on the efficiency of security and energy saving. The financial support is limited at a maximum of two kilns per each applicant. The promotional project also helps develop the human resources, provides knowledge and skills of ceramic firing and upgrades product quality to meet the international standards. The seminar and training on several issues such as raw material preparation, ceramic kiln control technique will be held for the operators, kiln makers and other people interested.
The highly efficient ceramic kiln is a fiber-lining kiln with specific attributes such as a lightweight and heat insulation. It can save the energy especially for the Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG), accounting for 30-50 percent compared with the old kilns (a refractory brick). The fiber-lining kiln not only improves the product quality in terms of color harmony and less wastes but also increases the capacity due to short period of firing.
Table 7: The Kiln Price of the Project and the Rate of Energy Saving
Kiln size The price Financial support Amount of The average
(cubic meters) determination of the payment for the rate of energy
project (baht) (34%) attendants (66%) saving
1.0 350,000 119,000 231,000 45.65%
1.5 450,000 153,000 297,000 N.A.
2.5 650,000 221,000 429,000 45.88%
4.0 800,000 272,000 528,000 52.00%
5.5 or above Negotiable price 289,000 Deductions 44.22% between buyers and sellers
Source: The Energy Efficiency Institute Thailand Foundation
Note: The kiln price is set at 40 baht quoted to the dollar. The average energy saving is based on the LPG
saving against the old kiln usage (a refractory brick)
3. The National Metal and Materials Technology Center of the National Science and Technology Development Agency, (Tel. 644-8150), will be pleased to provide consultations on research and development of ceramic products and to act as consultant and analyst in solving problems on the production process for the improvement of management and in providing services in carrying out tests and analyses of raw materials and products.
4. The Department of Metal Science, Faculty of science, Chulalongkorn University, in cooperation with a group of ceramic enterprisers, has set up the ceramic association of Thailand for the purposes of offering academic advice on ceramic and exchanging information and data between ceramic manufacturers and concerned department officials in order to overcome problems and develop the industry